2024-01-17 09:37:12
SPOTO Club
Cisco,CCIE Lab,CCNP,CCIE,CCNA
761
 Foreword:
Foreword:
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the Internet's phone book. Map IP addresses that are difficult for humans to remember to be relatively easy to remember in English, provide network services, and access information online through domain names such as nytimes.com or espn.com Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS converts domain names to IP addresses so that browsers can load Internet resources.
Each device connected to the Internet has a unique IP address that other computers can use to find the device. The DNS server does not require human memory IP addresses, such as 192.168.1.1 (in IPv4), or more complex new alphanumeric IP addresses, such as 2400: cb00: 2048: 1 :: c629: d7a2 (in IPv6).
DNS domain name structure
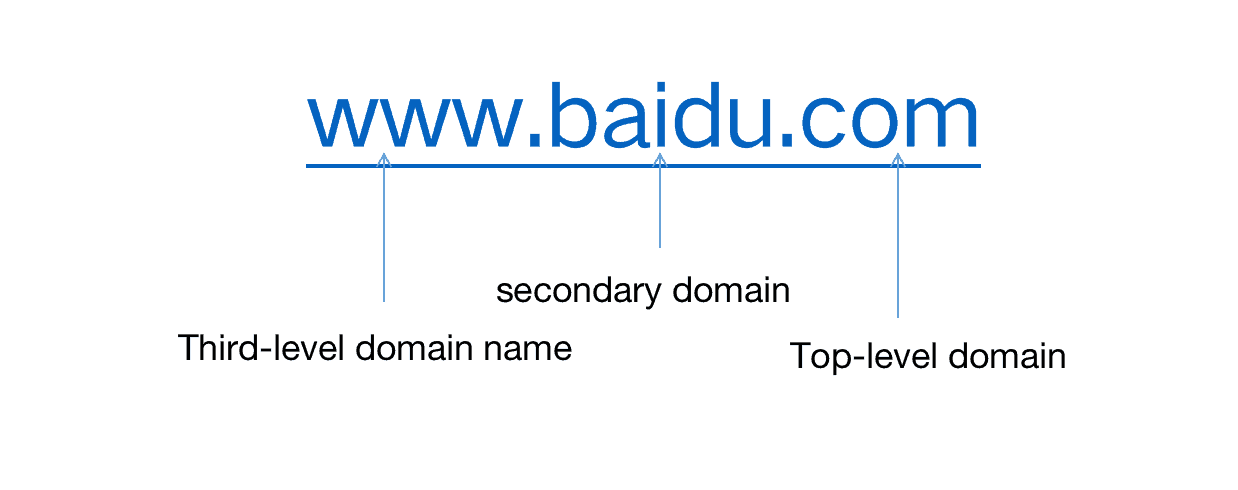
Each IP address can have a host name. The host name is composed of one or more character strings, and the strings are separated by a decimal point through the host name. The process of finally obtaining the IP address corresponding to the host name is called domain name resolution.
Generally, the domain name structure of an Internet host is: host name. Third-level domain name. Second-level domain name. Top-level domain name. The Internet's top-level domain name is registered and managed by the Internet Network Association's domain name registration query committee responsible for network address allocation. It also assigns a unique IP address to each host on the Internet.
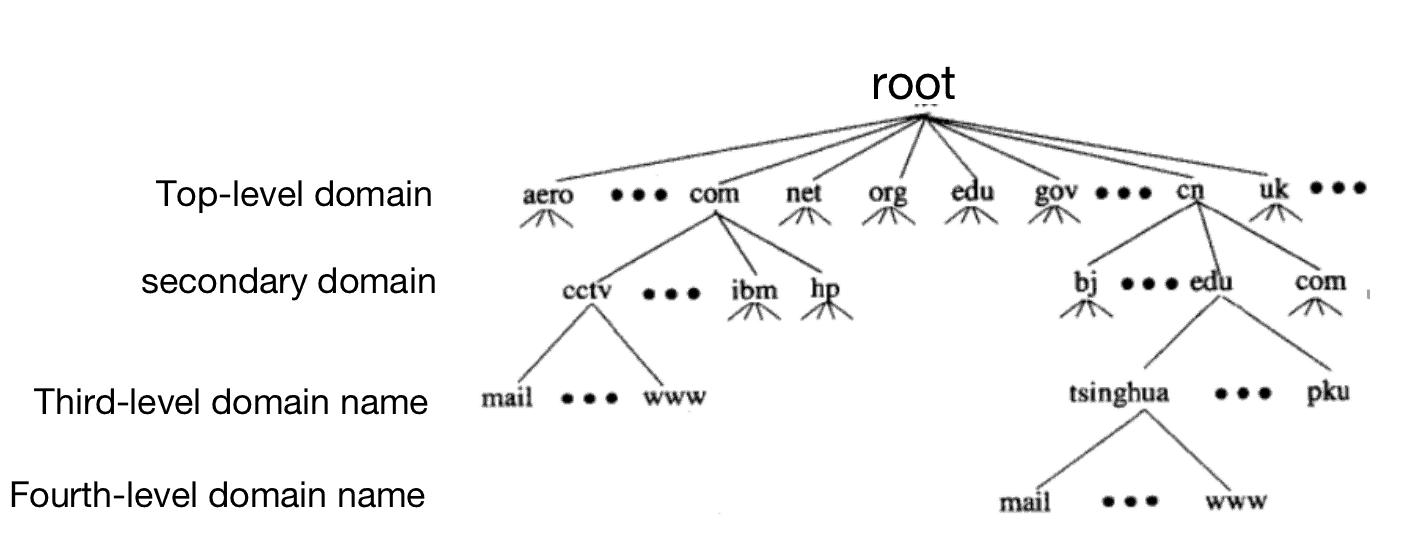 Top-level domain:
Top-level domain:
Cn --- is China
Us ---is the United States
Jp ---is Japan
secondary domain:
.com---Generally used for commercial institutions or companies
.net---Generally used for organizations or companies engaged in Internet-related network services
.top---generally used for enterprises and personal organizations
.org---generally used for non-profit organizations and groups
.gov---for government departments
How does DNS work?
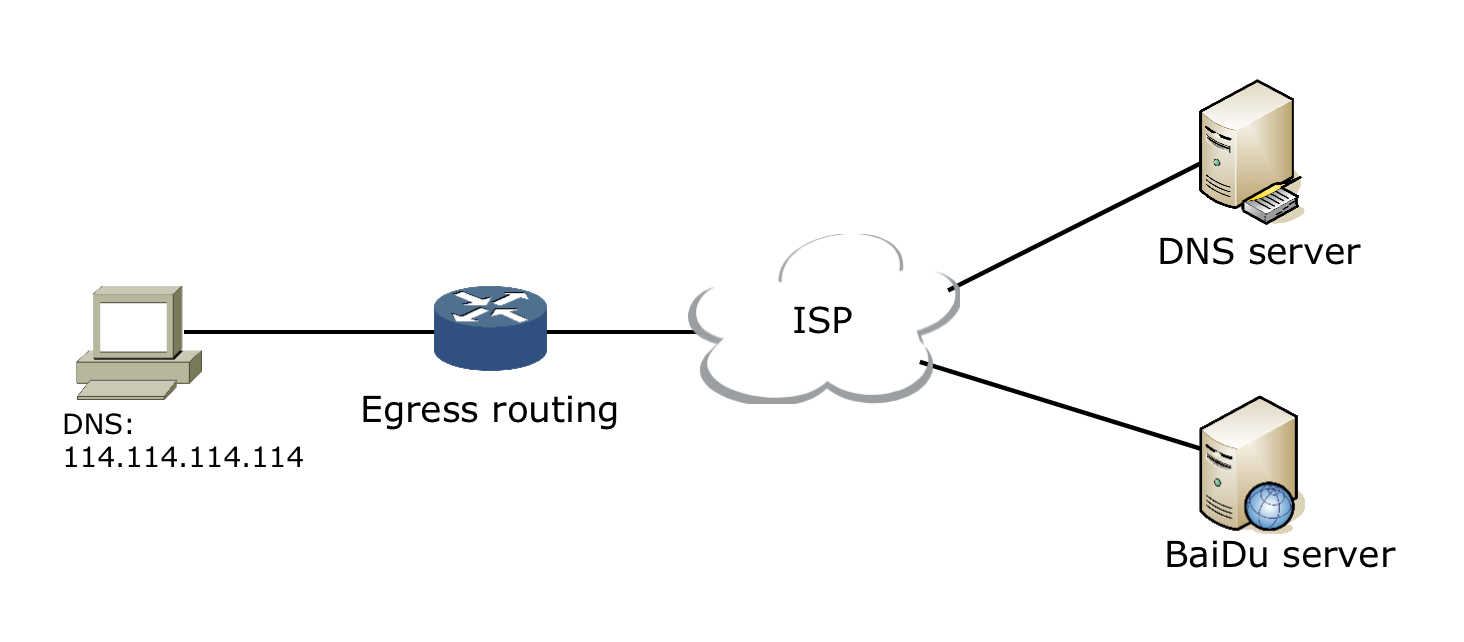
- Enter the www.baidu.com domain name in the browser. The operating system will first check whether its local hosts file has this URL mapping relationship. If so, it will first call this IP address mapping to complete the domain name resolution.
- If there is no mapping of this domain name in the hosts, then look up the local DNS resolver cache, if there is this URL mapping relationship, if there is, return directly to complete the domain name resolution.
- If there is no corresponding URL mapping relationship between the hosts and the local DNS resolver cache, we will first find the preferred DNS server set in the TCP / IP parameters, here we call it the local DNS server,
When this server receives the query, if the domain name to be queried is included in the local configuration area resource, it will return the resolution result to the client to complete the domain name resolution. This resolution is authoritative.
- If the domain name to be queried is not resolved by the local DNS server area, but the server has cached this URL mapping relationship, then this IP address mapping is called to complete the domain name resolution, which is not authoritative.
- If both the local zone file and the cache resolution of the local DNS server are invalid, query according to the settings of the local DNS server (whether or not to set a forwarder),
If the forwarding mode is not used, the local DNS will send the request to the "root DNS server". After receiving the request, the "root DNS server" will determine who the domain name (.com) is to authorize management and return a responsible domain name. An IP of the server.
After the local DNS server receives the IP information, it will contact the server responsible for the .com domain. After the server responsible for the .com domain receives the request, if it cannot resolve it,
It will find a lower DNS server address (baidu.com) that manages the .com domain to the local DNS server. When the local DNS server receives this address, it will find the baidu.com domain server, repeat the above actions, and query until it finds the www.baidu.com host.
- If the forwarding mode is used, the DNS server will forward the request to the upper-level DNS server for resolution by the upper-level server. , Cycle through this.
Regardless of whether the local DNS server is used for forwarding or root hints, the result is finally returned to the local DNS server, and then the DNS server is returned to the client.
Inquiry mode
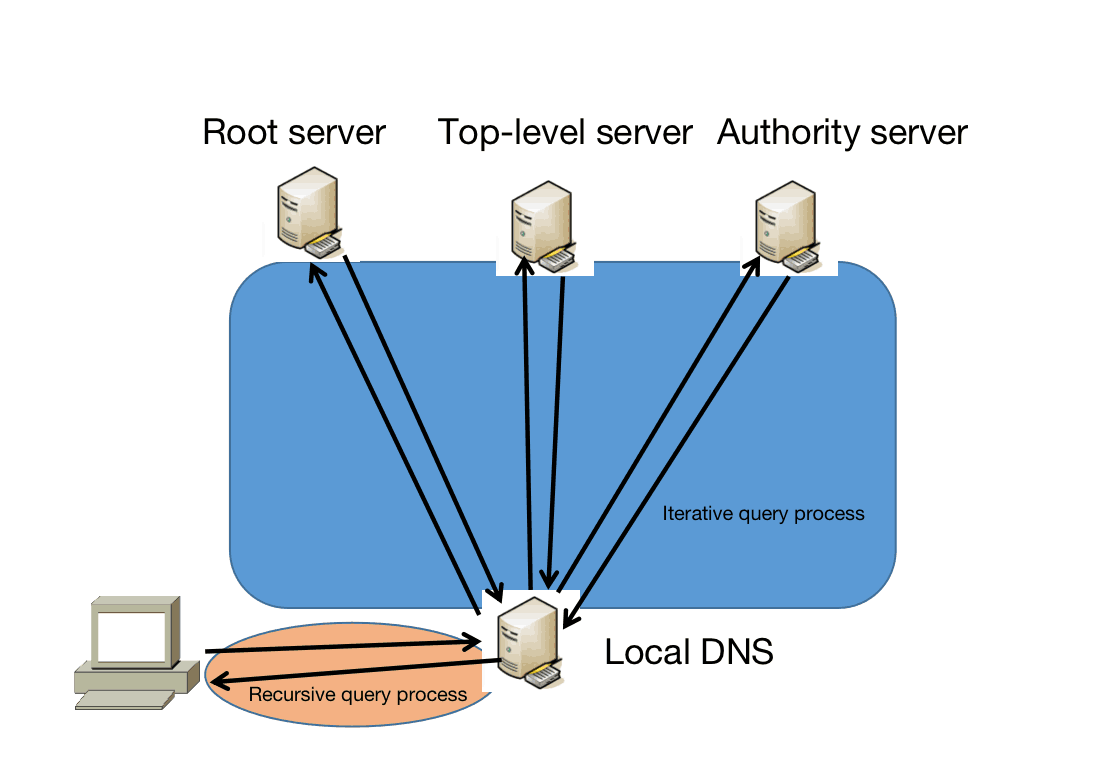
- The query from the host to the local domain name server is generally recursive.
The so-called recursive query is: if the local domain name server inquired by the host does not know the IP address of the domain name being queried, the local domain name server acts as a DNS client,
Instead of sending the host to perform the next query, it will continue to send query request messages to other root domain name servers (that is, continue to query for the host).
Therefore, the query result returned by the recursive query is either the IP address to be queried, or an error is reported, indicating that the required IP address cannot be queried.
A
- Iterative query of the local domain name server to the root domain name server.
Features of iterative query: When the root domain name server receives the iterative query request message from the local domain name server, it either gives the IP address to be queried or tells the local server: "Which domain name server should you query next" .
Then let the local server perform subsequent queries. The root domain name server usually tells the local domain name server the IP address of the top-level domain name server that it knows, and then the local domain name server queries the top-level domain name server.
After receiving the query request from the local domain name server, the top-level domain name server either gives the IP address to be queried, or tells the local server which authority domain name server to query next.
Finally, know the IP address to be resolved or report an error, and then return this result to the host that initiated the query
Basic configuration example
 SERVER (config) #ip dns server //Enable its own ability to resolve domain names
SERVER (config) #ip host r1 192.168.1.1 //On the DNS server, create a 'parse entry'
SERVER (config) #ip host r2 192.168.1.2 //On the DNS server, create a 'parse entry'
CLIENT (config) #ip name-server 192.168.1.1 //Set the DNS server, that is, point to the DNS server IP, when there is no resolution entry locally, iteratively query the next server
CLIENT # telnet r1
(Execute the telnet command to check)
Translating "r1"… domain server (192.168.1.1) [OK]
SERVER (config) #ip dns server //Enable its own ability to resolve domain names
SERVER (config) #ip host r1 192.168.1.1 //On the DNS server, create a 'parse entry'
SERVER (config) #ip host r2 192.168.1.2 //On the DNS server, create a 'parse entry'
CLIENT (config) #ip name-server 192.168.1.1 //Set the DNS server, that is, point to the DNS server IP, when there is no resolution entry locally, iteratively query the next server
CLIENT # telnet r1
(Execute the telnet command to check)
Translating "r1"… domain server (192.168.1.1) [OK]

 Foreword:
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the Internet's phone book. Map IP addresses that are difficult for humans to remember to be relatively easy to remember in English, provide network services, and access information online through domain names such as nytimes.com or espn.com Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS converts domain names to IP addresses so that browsers can load Internet resources.
Each device connected to the Internet has a unique IP address that other computers can use to find the device. The DNS server does not require human memory IP addresses, such as 192.168.1.1 (in IPv4), or more complex new alphanumeric IP addresses, such as 2400: cb00: 2048: 1 :: c629: d7a2 (in IPv6).
DNS domain name structure
Foreword:
The Domain Name System (DNS) is the Internet's phone book. Map IP addresses that are difficult for humans to remember to be relatively easy to remember in English, provide network services, and access information online through domain names such as nytimes.com or espn.com Web browsers interact through Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. DNS converts domain names to IP addresses so that browsers can load Internet resources.
Each device connected to the Internet has a unique IP address that other computers can use to find the device. The DNS server does not require human memory IP addresses, such as 192.168.1.1 (in IPv4), or more complex new alphanumeric IP addresses, such as 2400: cb00: 2048: 1 :: c629: d7a2 (in IPv6).
DNS domain name structure
 Each IP address can have a host name. The host name is composed of one or more character strings, and the strings are separated by a decimal point through the host name. The process of finally obtaining the IP address corresponding to the host name is called domain name resolution.
Generally, the domain name structure of an Internet host is: host name. Third-level domain name. Second-level domain name. Top-level domain name. The Internet's top-level domain name is registered and managed by the Internet Network Association's domain name registration query committee responsible for network address allocation. It also assigns a unique IP address to each host on the Internet.
Each IP address can have a host name. The host name is composed of one or more character strings, and the strings are separated by a decimal point through the host name. The process of finally obtaining the IP address corresponding to the host name is called domain name resolution.
Generally, the domain name structure of an Internet host is: host name. Third-level domain name. Second-level domain name. Top-level domain name. The Internet's top-level domain name is registered and managed by the Internet Network Association's domain name registration query committee responsible for network address allocation. It also assigns a unique IP address to each host on the Internet.
 Top-level domain:
Cn --- is China
Us ---is the United States
Jp ---is Japan
secondary domain:
.com---Generally used for commercial institutions or companies
.net---Generally used for organizations or companies engaged in Internet-related network services
.top---generally used for enterprises and personal organizations
.org---generally used for non-profit organizations and groups
.gov---for government departments
How does DNS work?
Top-level domain:
Cn --- is China
Us ---is the United States
Jp ---is Japan
secondary domain:
.com---Generally used for commercial institutions or companies
.net---Generally used for organizations or companies engaged in Internet-related network services
.top---generally used for enterprises and personal organizations
.org---generally used for non-profit organizations and groups
.gov---for government departments
How does DNS work?


 SERVER (config) #ip dns server //Enable its own ability to resolve domain names
SERVER (config) #ip host r1 192.168.1.1 //On the DNS server, create a 'parse entry'
SERVER (config) #ip host r2 192.168.1.2 //On the DNS server, create a 'parse entry'
CLIENT (config) #ip name-server 192.168.1.1 //Set the DNS server, that is, point to the DNS server IP, when there is no resolution entry locally, iteratively query the next server
CLIENT # telnet r1
(Execute the telnet command to check)
Translating "r1"… domain server (192.168.1.1) [OK]
SERVER (config) #ip dns server //Enable its own ability to resolve domain names
SERVER (config) #ip host r1 192.168.1.1 //On the DNS server, create a 'parse entry'
SERVER (config) #ip host r2 192.168.1.2 //On the DNS server, create a 'parse entry'
CLIENT (config) #ip name-server 192.168.1.1 //Set the DNS server, that is, point to the DNS server IP, when there is no resolution entry locally, iteratively query the next server
CLIENT # telnet r1
(Execute the telnet command to check)
Translating "r1"… domain server (192.168.1.1) [OK]
